Does IFRS 17 encourage Asset-Liability-Management in Insurance?
View this page in: Chinese (Traditional)
Based on PwC’s IFRS 17 Health Check Survey 2021: Asia Pacific, 50% of the respondents indicated that IFRS 17 will be the main basis for driving their organizations’ business strategy. Beyond business strategy, a vast majority of respondents have not started thinking about how IFRS 17 will affect their risk management, investment strategy, pricing methodology, product mix, reinsurance management strategy, and capital requirement. This is perhaps not surprising because the majority of effort is being spent on getting the core primary statements and disclosures right in accordance with the IFRS 17 standard itself.
Do you expect the following items to change due to the implementation of IFRS 17?
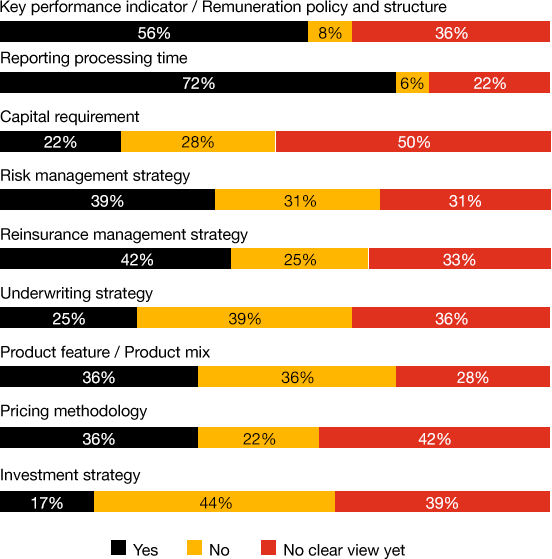
Source: PwC’s IFRS 17 Health Check Survey 2021: Asia Pacific, May 2021
Under IFRS 17, insurance liabilities are required to be evaluated at observable current market rate, i.e., the fair value of insurance liabilities. It enhances the transparency for asset and liability mismatching risks including currency and duration mismatches which result in volatilities of financial earnings and solvency. Take Taiwan Dollar denominated insurance liabilities as an example, 10-year present value of $1,000 at locked rate of 6% is $558 which will turn into $905 at current market rate of 1%, i.e., 1.6 times. Besides, the asset and liability mismatches (ex: 10-year bonds to support 30-year insurance liabilities) are expected to enlarge volatilities in the company’s financial earnings and solvency. From the IMF’s chart below, it shows that APAC life insurance companies suffer more in the spread (a driver for currency mismatch, i.e., US assets to support local liabilities) and duration mismatch issues.

Source: IMF Global Financial Stability Report - Lower for Longer, Oct 2019
It is important for insurance companies to think about the following questions for the upcoming IFRS 17 implementations:

What do you see as key challenges and opportunities for your operations if IFRS 17 were implemented? (Ex: How to manage the earning/capital volatilities by improving asset and liability management?)

How are your competitors reacting in key areas such as strategy, investments, risk management, products in anticipation of implementation of IFRS 17? (Ex: Transfers long-term guaranteed products to protection/variable products; aligns investment strategy better with its liability profile to well manage interest rate risk)
What are your recommended approaches to mitigate risks/capitalize on opportunities/address challenges to the business? (Ex: Should we consider interest rate derivatives? Does our reinsurance arrangement still fit to the company’s needs?)
Asset-Liability-Management (ALM)
It becomes clear that Asset-Liability-Management is a key solution which targets to maximize economic value under given risk tolerance for the upcoming IFRS 17 implementation to achieve a company’s business objectives. ALM shall be embedded in each business function especially for product & liability management, investment strategy and capital management. It is crucial to build/enhance the dialogue between investment and product teams, i.e., “investment driven product development” and “liability driven investment strategy”. PwC has a thorough ALM Framework to help our client to build/enhance its ALM effectiveness and further develop related business strategies. This is also what we helped/are helping our clients. Get in touch with the authors or your local PwC team to hear how our ALM Framework could help you.

Contact us






